(Sun)dew the July quiz! All our questions are based on our science stories from the last month. Image: Mat Gilfedder.
It’s the end of the July and we’re officially in the second half of the year! Yay! Give yourself a pat on the back.
So one thing about this month is that it went extremely fast. It was almost blink and you miss it.
But have you been paying attention to the science stories we’ve put out? We’re putting you to the test! No buzzers or Aussie comedians here.
Chuck on your favourite Spotify playlist and get ready. It’s July quiz time.
Results
#1. Our lab-grown airway cells could change how we understand respiratory diseases. Where are the donated cells from in the human body?
It’s a! The research was published in the journal Viruses in early July. Our lab-grown airway cells could help minimise the need for animal testing and fast-track new treatments for human trials. You can read more about how our scientists did this here.

#2. BHP Foundation Science and Engineering Awards finalist Angela Rofail’s engineering project is inspired by a certain animal. Which one?
It’s c! Angela noticed the shape of a crocodile’s back and used this design for her project on high rise buildings. The crocodile-inspired knobs reduced the movement of the model when subjected to strong winds. Read more about Angela’s project here.
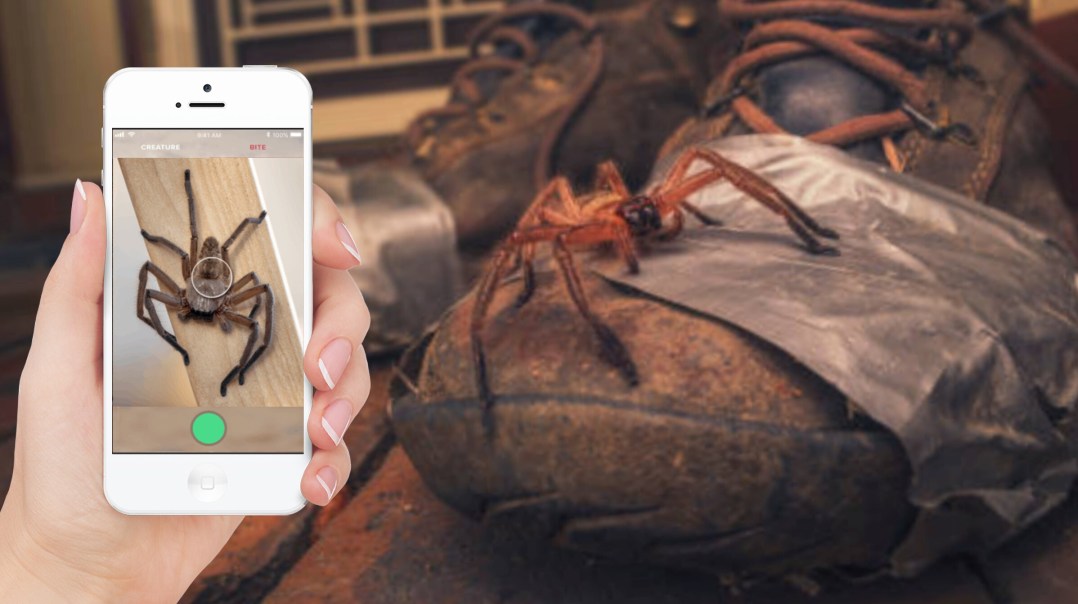

#3. Data61 is collaborating on a tool to help you take the guesswork out of identifying a spider or snake. What's the app called?
It’s d! Critterpedia combines machine learning and citizen science. It uses an algorithmic solution to identify the species of spider or snake submitted by users. Read more about Critterpedia here.
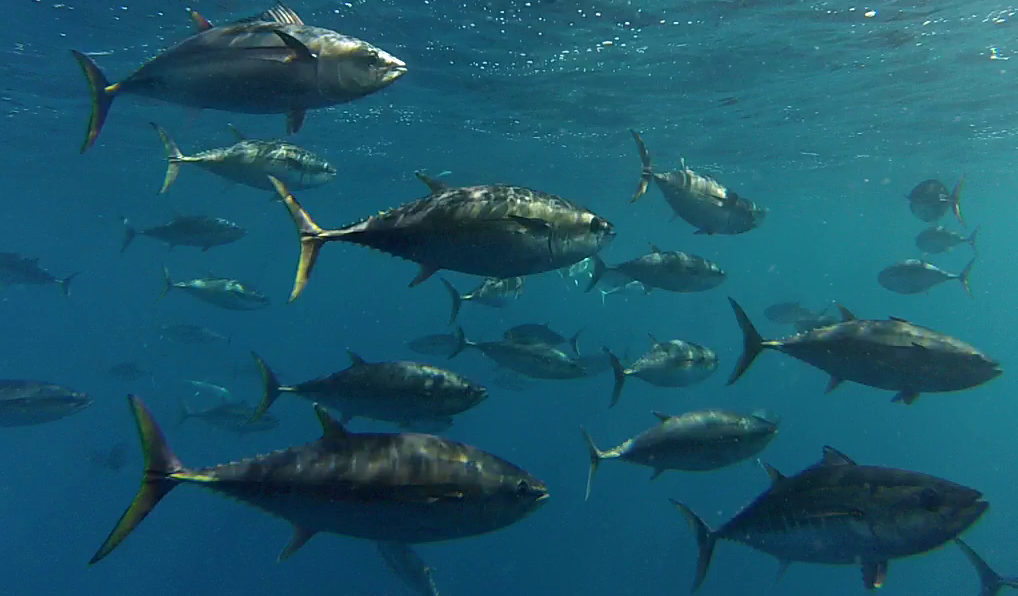

#4. Recreational fishers have recaptured a southern bluefin tuna we tagged in the Great Australian Bight. What year did we tag this fish?
It’s c! It’s the oldest southern bluefin tuna ever recaptured after tagging, and longest ‘days at liberty’ for a tagged fish. See how this fish helped our research and how we’re moving away from traditional tagging here.

#5. Our mathematicians have used their skills for interesting careers. Which field don’t they currently work in?
It’s a! Maths careers can be anything but average. Five of our mathematicians sat down and told us how they used maths to get to where they are. Read more about that here.

#6. Which of these is not a type of cybersecurity attack?
It’s a! Humans are the weakest link when it comes to cybersecurity attacks. We give you the low down on what these terms mean and how to avoid something “phishy” here.
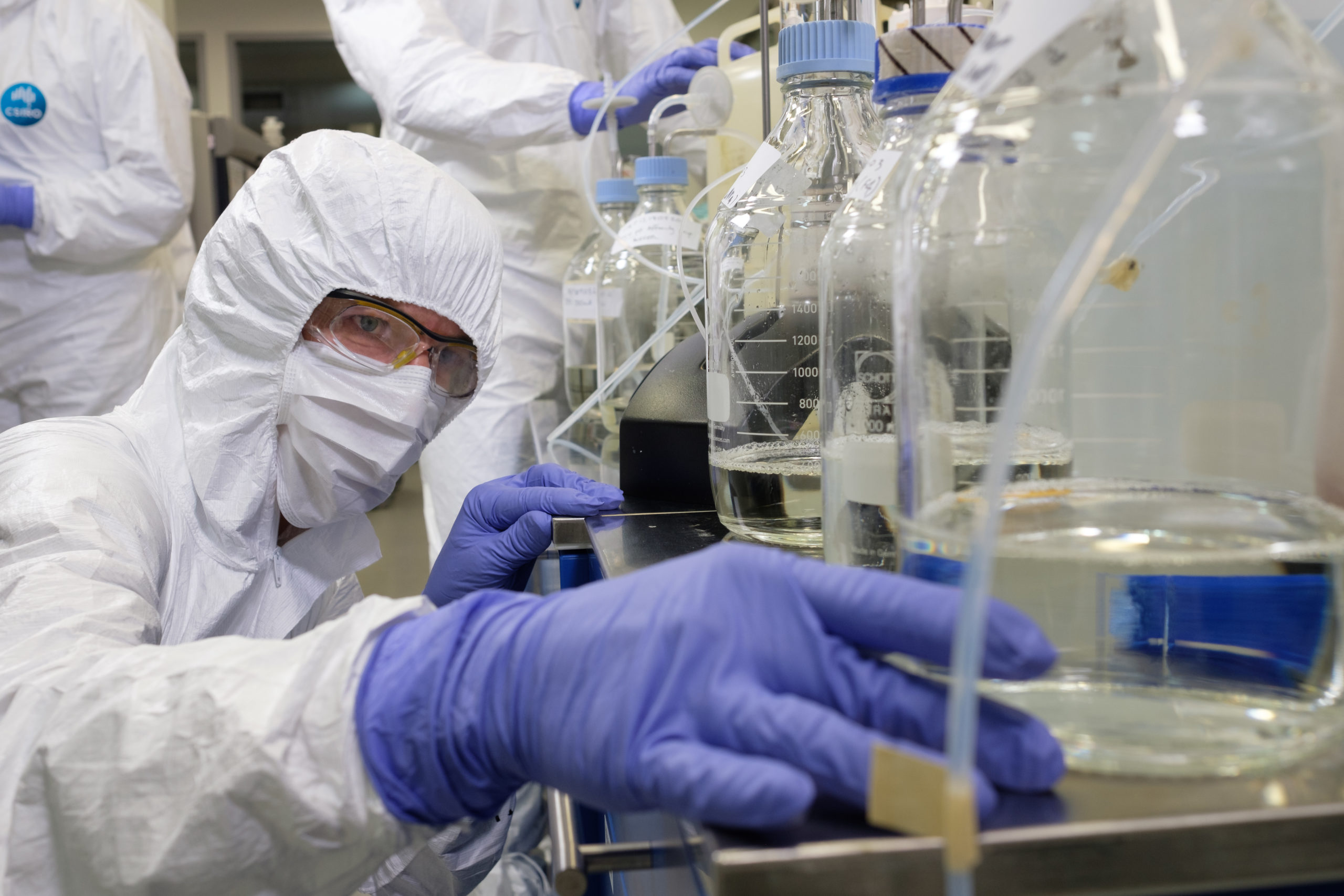

#7. We're manufacturing a COVID-19 vaccine candidate in our labs. Where is this vaccine candidate from?
It’s b! Scientists at our state-of-the-art biologics production facility in Melbourne are working on producing and scaling-up The University of Queensland’s (UQ) COVID-19 vaccine candidate. See how they’re making more of this vaccine candidate which is still safe and effective here.
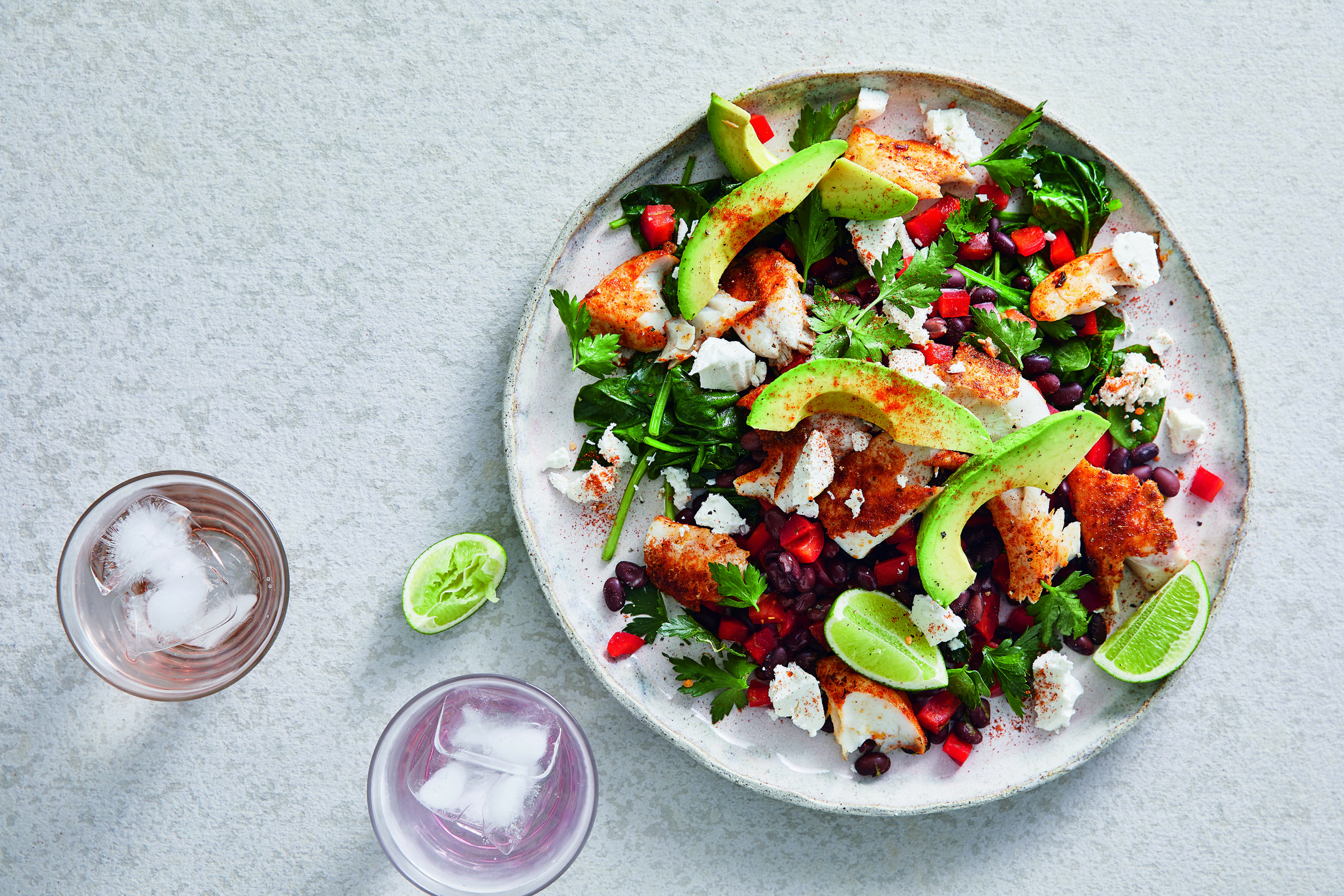

#8. Which factor increases our risk of developing type 2 diabetes?
It’s b! Type 2 diabetes is one of the greatest global health challenges of the 21st century. And it accounts for about 85-90 per cent of all diabetes cases. Our low carb diet can help manage this disease. Read more here or pre-order our new CSIRO Low Carb Diabetes Diet and Lifestyle Solution Book here.
#9. We’re partnering with industry to develop a vegan-friendly Omega-3 oil! Where are we getting these oils from?
It’s a! We produce the marine-derived Omega-3s using specific strains of unique thraustochytrids. These are a single-cell marine organism. As well as being vegan-friendly, it will offer a more sustainable option for consumers. Read more about our work and our partnership here.
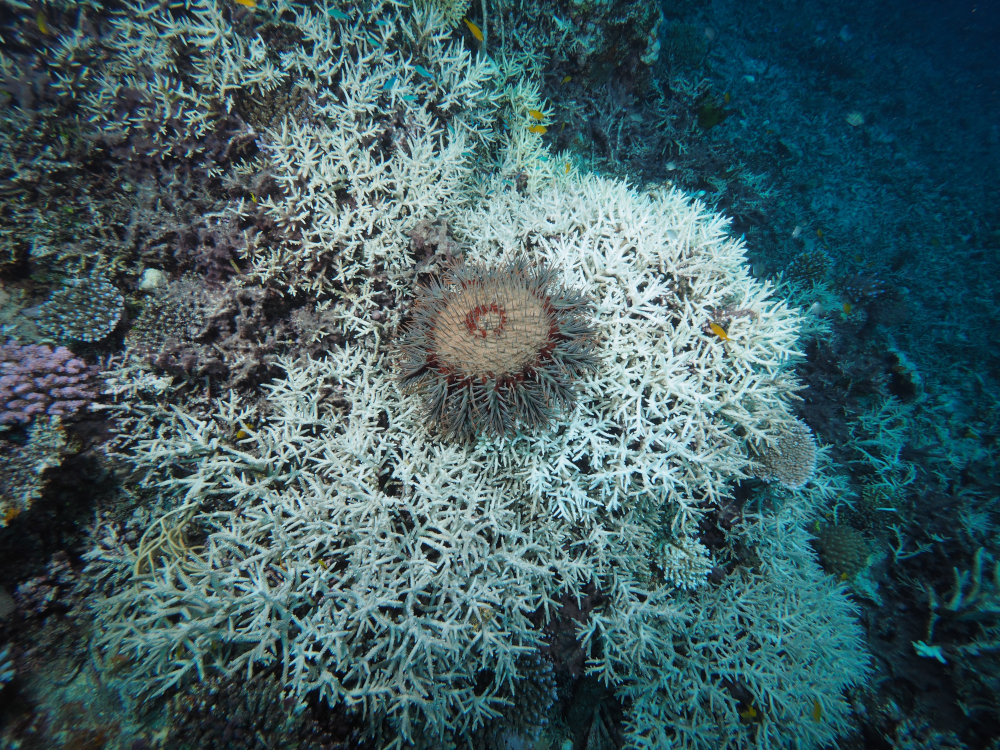

#10. The crown of thorns starfish is a pest in the Great Barrier Reef. What pantry staple are we using to stop this starfish in its tracks?
It’s b! Divers inject the crown of thorns starfish with either vinegar or bile salt solution and leave them in place on the reef. These techniques kill quickly and effectively with no negative impacts on the marine environment. Vinegar has helped manage these starfish so they no longer consume coral faster than it can grow back. Read more here.
How did you go in the July quiz?
July-ke your score? Let us know how you went in the comments below.
If you want to improve your score for next month, we’ve got an easy fix for you. Just tune in to our social channels or subscribe so you’ll never miss out!
We’ll be waiting for you until next time. See you then!




